Last Updated on May 29, 2024 by Alarm New England
In an age where security is paramount, access control systems have evolved significantly. Biometric access control, once relegated to the realms of science fiction, is now a reality. This technology not only enhances security but also streamlines access for authorized personnel in high-traffic areas, making it a game-changer in the field of security and access management.

The Evolution of Access Control
Traditional access control methods, such as ID cards, PINs, and keys, have their limitations. These methods are susceptible to theft, duplication, or unauthorized sharing, compromising security. Moreover, managing access for large numbers of people in high-traffic areas can be a logistical nightmare.
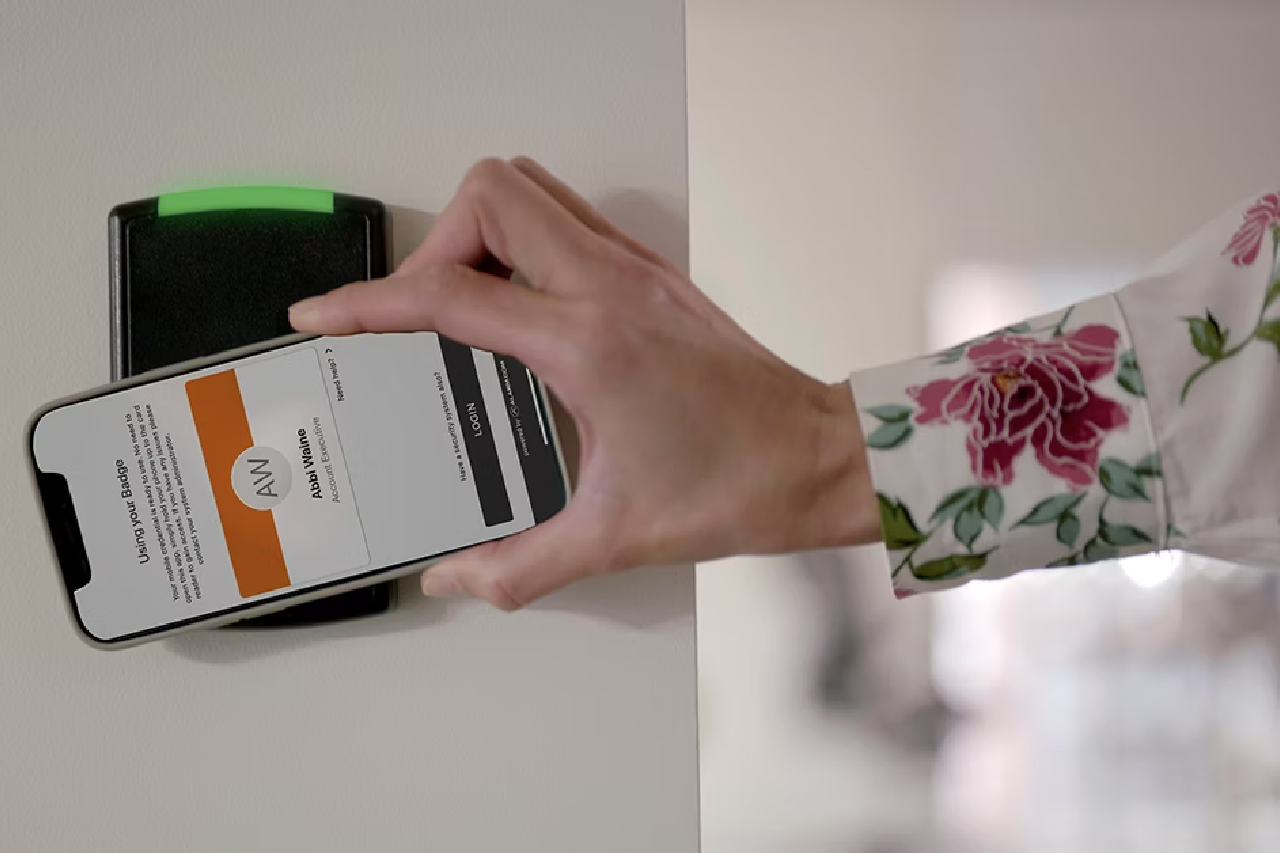
Biometric access control systems, on the other hand, use unique physical or behavioral characteristics to grant or deny access. These characteristics include fingerprints, facial recognition, iris scans, and even voice recognition. Unlike traditional methods, biometric data is incredibly difficult to duplicate or forge, making it a robust solution for high-security environments.
Why Biometric Access Control For Areas of High Traffic?
1. Unparalleled Security
Biometric access control systems provide a level of security that is unmatched by traditional methods. For instance, fingerprint recognition ensures that only individuals with authorized fingerprints can gain access. This eliminates the risk of stolen or lost ID cards being used by unauthorized personnel. Additionally, the high accuracy of biometric recognition reduces the likelihood of false positives, where authorized individuals are denied access, or false negatives, where unauthorized individuals gain entry.
2. Convenience and Speed
In high-traffic areas, speed and convenience are crucial. Biometric access control systems excel in this regard. With a quick scan of a fingerprint or a glance at a facial recognition camera, authorized personnel can gain entry swiftly and efficiently. This eliminates the need for time-consuming card swipes or manual identity verification, reducing congestion and wait times.
3. Elimination of Human Error
Traditional access control systems often rely on human operators to verify credentials manually. This introduces the risk of human error, such as misreading ID cards or overlooking security breaches. Biometric systems, being automated, significantly reduce the margin for error, ensuring consistent and reliable security.
4. Scalability
High-traffic areas can see a constant influx of personnel, from employees to visitors. Biometric access control systems are easily scalable to accommodate this fluctuation in traffic. Adding or removing individuals from the system is straightforward, and there’s no need to issue new physical access cards or change PIN codes, simplifying the management of access permissions.
5. Keeping an Access Record
Biometric access control systems offer comprehensive audit trails, providing detailed records of who accessed an area, at what time, and for how long. This feature is invaluable for security personnel and administrators, as it allows for real-time monitoring and quick response to security incidents. In the event of a breach, identifying the responsible party becomes much easier with biometric data.
Implementing Biometric Access Control
Deploying a biometric access control system in a high-traffic area like an airport or healthcare facility requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations:
- System Selection: Choose the biometric recognition method that best suits your needs and budget. Fingerprint and facial recognition are the most common choices, but other options like iris scans and voice recognition may be suitable depending on the specific requirements.
- Integration: Ensure that the biometric access control system integrates seamlessly with your existing security infrastructure, including surveillance cameras, alarms, and door hardware. This integration enhances overall security and provides a holistic approach to access control.
- User Enrollment: Enroll authorized personnel into the system by capturing their biometric data. This process must be conducted with care to ensure accuracy and privacy compliance. Data protection regulations must be strictly adhered to, and individuals should be informed about how their biometric data will be used and stored.
- Backup Mechanisms: While biometric systems are highly reliable, it’s important to have backup mechanisms in place in case of system failures or emergencies. This can include PIN codes or smart cards for redundancy.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Regular maintenance and software updates are essential to keep the biometric access control system functioning optimally. This includes calibrating cameras and sensors, updating biometric templates, and ensuring that the database is secure.
Looking Ahead at Biometric Access Control
As technology continues to advance, biometric access control is poised to become even more sophisticated and versatile. Future developments may include:
Contactless Biometrics: In response to global health concerns, contactless biometric systems are gaining traction. These systems can perform recognition without physical contact, reducing the risk of disease transmission.
Behavioral Biometrics: Beyond physical traits, behavioral biometrics, such as keystroke dynamics or gait analysis, are being explored for authentication. This adds an extra layer of security and makes it more difficult for malicious actors to bypass access controls.
Artificial Intelligence: Integration with artificial intelligence (AI) can enhance biometric systems’ ability to detect anomalies and suspicious behavior. AI can also improve recognition accuracy and speed.
The Bottom Line
Biometric access control is a game-changer for high-traffic areas, offering unparalleled security, convenience, and scalability. By eliminating the vulnerabilities associated with traditional access control methods, biometrics provide a robust solution for modern security challenges. As technology continues to evolve, biometric access control systems will only become more sophisticated and integral to install in high-traffic areas in an increasingly interconnected world.