Creating a safe home environment is essential. Whether you live in a house in the suburbs or an apartment in the city, these safety tips will help make your home more secure. If you’ve ever wondered how to stay safe at home, you would do well to follow these tips for better security and peace of mind.
Tip 1: Install a Security System
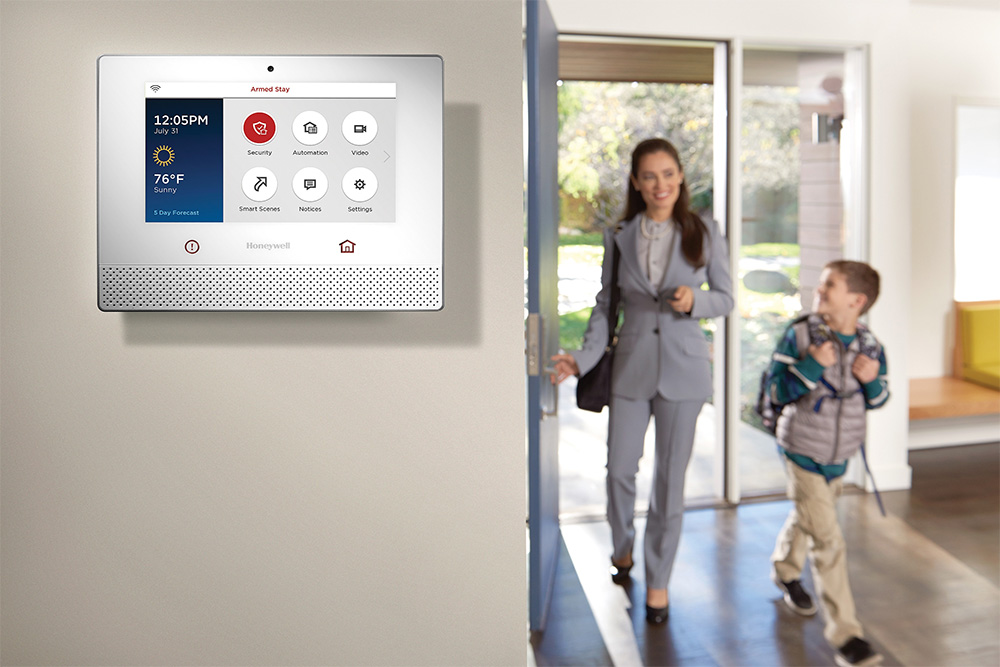
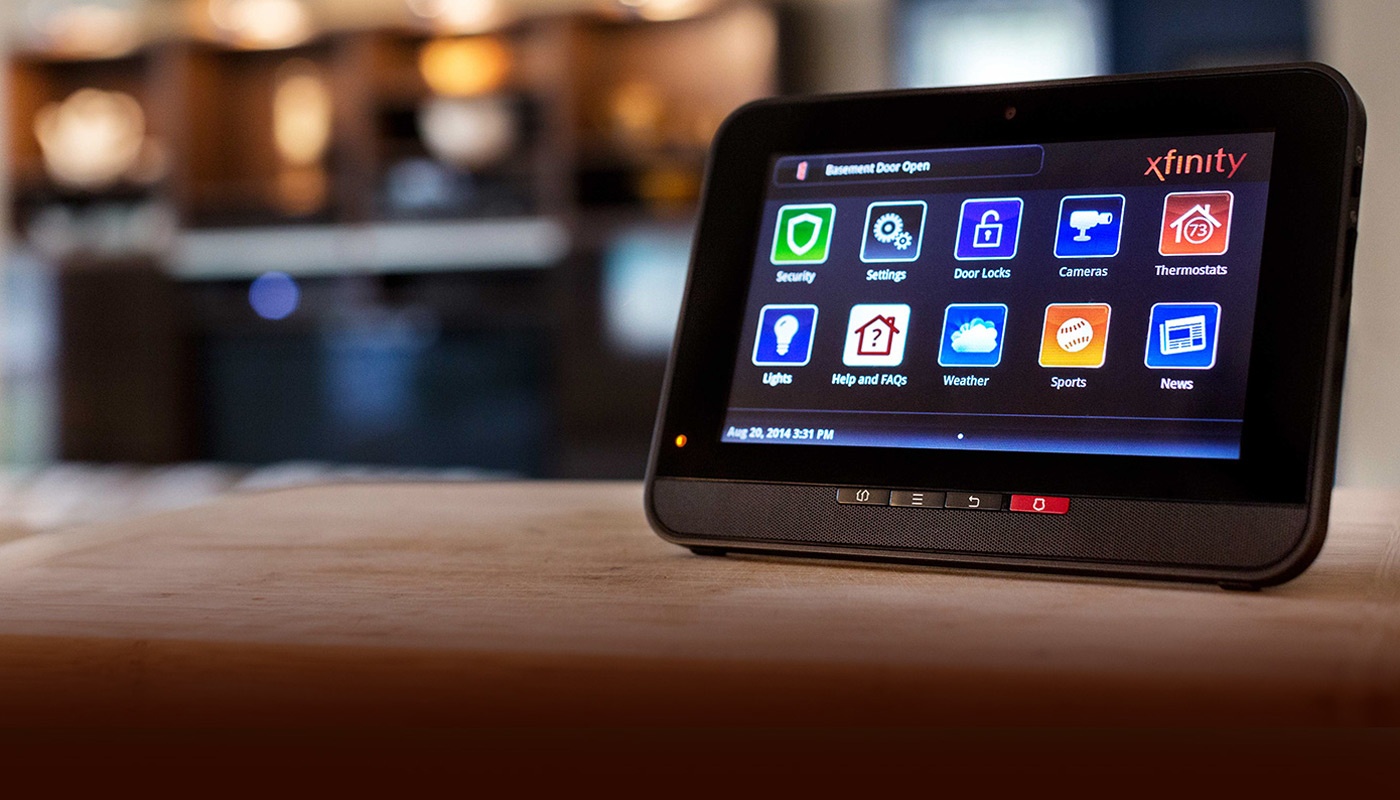
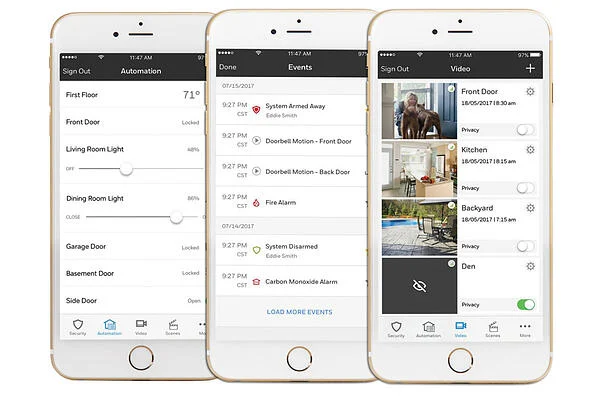
Perhaps the most straightforward course of action, installing a security system is a no-brainer for those wanting to stay safer at home. And there’s never been a better time to invest in home security. Modern home security systems do more than just deter intruders, they also allow for the best possible response in an emergency situation. A security company will help you install sensors at all entry points and test them regularly. The best systems include 24/7 professional monitoring, ensuring your home is protected even when you’re asleep or away.
Many modern systems also offer smartphone integration, allowing you to monitor your home’s security status from anywhere in the world. These systems make home security easier and more effective than ever. And the integrated nature of newer system expands your range of possibilities for smarter and more efficient home.
Tip 2: Stay Safe with a Video Doorbell
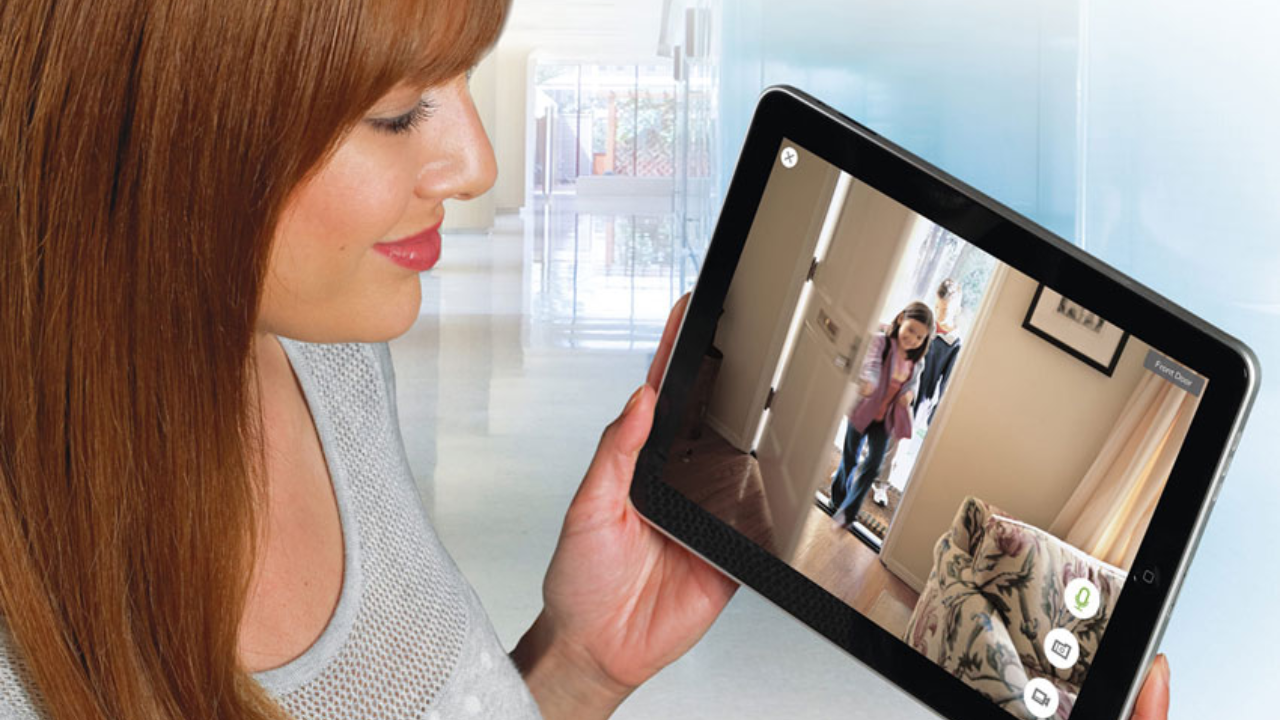
A newer innovation in home security is the video doorbell camera. A video doorbell serves as your first line of defense against potential threats at your front door. These devices allow you to see, hear, and speak with visitors without opening your door or even being home. With HD video and two-way audio capabilities, you can safely manage package deliveries, screen unexpected visitors, and maintain a recorded history of everyone who approaches your door.
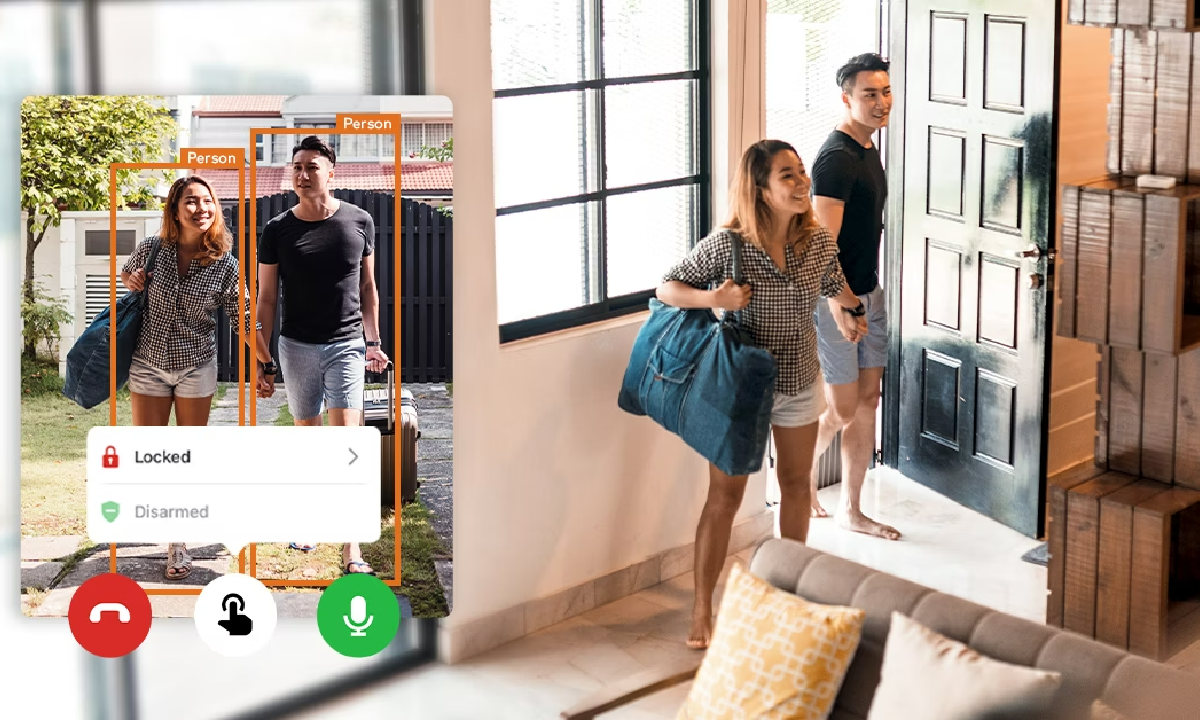

Some of the best video doorbells include features like motion detection, night vision, and wide-angle views that eliminate blind spots. They can send instant alerts to your smartphone when someone approaches your door, allowing you to take immediate action if needed. Many models also offer cloud storage of video footage, providing valuable evidence in case of security incidents.
Alarm New England offers state-of-the-art video doorbell solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing security system. Our expert team can help you choose and install the perfect video doorbell for your home’s specific needs.
Tip 3: Get Smart Locks for Better Home Safety
While basic door locks have served us well for centuries, smart locks represent a significant leap forward in home security technology. These devices allow you to control and monitor your doors remotely through your smartphone, eliminating the worry of forgotten keys or unlocked doors.
One of the most valuable features of smart locks is the ability to verify your door’s status from anywhere. Lying in bed and wondering if you locked the front door? Simply check your phone and lock it remotely if needed. Expecting a delivery while at work? You can temporarily grant access and then ensure the door is secured afterward, all from your smartphone.
Transform your home’s security with a smart lock installed by Alarm New England. Our professional team can help you select and install the perfect smart lock system, connecting it seamlessly with your existing security setup for your best protection and convenience.
Tip 4: Don’t Forget Perimeter Security
It sounds complicated, but perimeter security is a simple (and important) consideration at home. Your home’s exterior is the first line of defense against potential security threats, and proper planning can significantly enhance your safety. Start by evaluating your home’s perimeter security. Things like motion-sensing lights near all entry points can ward off potential intruders. Remember to position these lights high enough to prevent tampering.
There’s nothing simpler than some good old physical security too. A high quality gate or fence around your property can be a simple, yet extremely effective way to keep unwanted visitors out. A fence or secured gate is one more layer someone will need to pass through to reach your home. Simply the presence of a barrier might be enough to deter any unwanted trouble.

Tip 5: Make an Emergency Plan (Child and Adults)
An emergency plan can mean the difference between panic and measured response during a crisis. Consider various scenarios – what if your primary exit is blocked? Where would you go?
Make sure family members (especially children) understand the emergency plan too. Create an emergency contact list including local authorities, utility companies, medical providers, and trusted neighbors and store it somewhere easily accessible. Make sure that young children know who to contact in an emergency.
It’s also not a bad idea to keep a storage of essential supplies like water, non-perishable food, medications, first-aid supplies, and battery-powered flashlights. Review and update these kits regularly, replacing any expired items.
Tip 6: Protect Your Digital Security
Today, digital security has become as important as physical security. Start by securing your home’s wi-fi network with a strong password and encryption if available. Regularly update passwords for all smart home devices, and avoid using the same password across multiple devices or accounts.
Consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt your internet traffic and protect your personal information from cybercriminals.
Tip 7: Don’t Neglect Fire and Life Safety Systems
Beyond just a burglar alarm system or cameras, equip your home with smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors on every level, including inside and outside sleeping areas. These crucial devices will alert you at the first sign of smoke or a dangerous carbon monoxide leak. You can even keep fire extinguishers readily accessible on each floor in case of emergency.

You can also consider installing water leak detectors in susceptible areas like bathrooms and laundry rooms.
Tip 8: Networking with your Neighbors
Building a strong community network enhances everyone’s security. Establish relationships with neighbors and participate in or create a neighborhood watch program. Share emergency contact information with trusted neighbors who can check on your home during vacations or alert you to any suspicious activity.
Platforms like Nextdoor and Ring Neighbors are great for this. This network can be great for quick, far-reaching communication, and bringing awareness to issues that might affect homes in the neighborhood.
Tip 9: Keep Your House Well-Lit at Night
Proper lighting at night is one of the most effective yet often overlooked aspects of home security. Well-lit exteriors significantly reduce the risk of break-ins by eliminating potential hiding spots and making suspicious activity more visible to both residents and neighbors. Motion-activated lights are particularly effective, as they can startle intruders and draw immediate attention to movement around your property.
Beyond security, good outdoor lighting serves multiple practical purposes that enhance your home’s safety and livability. It prevents accidents by illuminating areas like steps and uneven walkways, which otherwise could cause trips and falls.
Tip 10: Provide Medical Pendants If Necessary
For homes with elderly family members or individuals with disabilities, medical alert systems provide crucial protection and peace of mind. Modern medical alert pendants offer features like fall detection, GPS tracking, and immediate connection to emergency services. These devices can be lifesaving in situations where someone is unable to reach a phone or call for help.
Need immediate access to emergency help? Alarm New England’s security system offers an in-app panic button feature accessible right from your smartphone. This convenient solution ensures help is always just a tap away, whether you’re at home or on the go. Contact us to learn how we can integrate this feature into your home security system.
Remember, home security isn’t a one-time effort – it requires regular care and attention. By following these tips and staying vigilant, you can create a safer environment for everyone who lives under your roof. The investment in home security today can prevent costly and dangerous situations tomorrow.
Want Tips from an Expert?
Call Alarm New England today for a free home security quote. You can reach our team at (857) 445-4010.











![[2026] 5 Best PTZ Security Cameras for Using Outdoors and Indoors](https://alarmnewengland.com/wp-content/uploads/amcrest-ptz-security-camera-ultrahd-1.png)









